In the evolving landscape of global finance, Bitcoin has emerged as a new asset class, prompting entities ranging from individuals to nations to consider it as part of their reserve strategies. Bitcoin reserve strategy involves holding Bitcoin in reserve assets to achieve objectives such as diversification, inflation hedging, and capital appreciation. This overview explores the concept, components, examples, risks, benefits, and future outlook of Bitcoin reserve strategies, providing a holistic understanding of its role in modern finance.
Definition and Objectives
Bitcoin reserve strategy refers to the systematic allocation of Bitcoin to an entity’s reserve – assets traditionally held in gold, foreign currencies, or Treasury bonds. Unlike traditional reserves, Bitcoin offers decentralization, scarcity, and censorship resistance. The primary objectives include:
- Diversification: Reducing reliance on traditional assets prone to inflation or geopolitical risks.
- Inflation Hedge: Bitcoin’s limited supply (21 million) is unlike fiat currencies, which central banks can devalue through excessive printing.
- Speculative Growth: Taking advantage of the potential for high returns seen in Bitcoin’s historical performance.
This strategy is particularly attractive in an era of macroeconomic uncertainty, where traditional reserves may underperform.
Components of a Bitcoin Reserve Strategy
- Allocation and Diversification
Determining the proportion of Bitcoin in reserves is important. While some institutions, such as MicroStrategy, allocate more than 90% of their treasury to Bitcoin, others take a conservative approach (1-5%). The allocation depends on risk tolerance, investment horizon, and market outlook. Diversification across asset classes (for example, combining Bitcoin with bonds or gold) reduces volatility risks. - Storage and Security
Securing Bitcoin requires robust solutions:
- Cold Wallets: Offline storage (e.g., hardware wallets) to prevent hacking.
- Multi-Signature Wallets: Transactions require multiple approvals.
- Institutional Custodians: Services like Coinbase Custody provide insured storage for large holdings.
Security breaches (e.g., the Mt. Gox hack) underscore the importance of stringent measures.
3. Risk Management
Bitcoin’s volatility (e.g., 70%+ price fluctuations in 2022) requires strategies such as the following:
- Hedging: Using derivatives or stablecoins to offset losses.
- Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA): Sequential purchases to minimize timing risk.
- Liquidity Buffer: Maintaining fiat reserves to avoid forced selling during a recession.
4. Regulatory Compliance Entities must navigate evolving regulations, including tax reporting (e.g., capital gains in the U.S.), anti-money laundering (AML) laws, and jurisdiction-specific bans. Proactive engagement with regulators is essential
5. Liquidity Management While Bitcoin is liquid compared to real estate, large sales can impact market prices. Entities must Balance liquidity needs with long-term holding strategies.
Examples of Bitcoin Reserve Strategies
- Corporate Adoption
- MicroStrategy: Tech firm holds ~190,000 BTC (by 2023), sees Bitcoin as a superior treasury reserve to cash. CEO Michael Saylor advocates Bitcoin as “digital gold.”
- Tesla: Briefly allocated $1.5 billion to Bitcoin in 2021, highlighting both opportunities and risks when it sold 10% of its holdings during market turmoil.
2. National Adoption
- El Salvador: Became the first country to adopt Bitcoin as a legal currency in 2021, purchasing 2,798 BTC. Despite criticism over volatility and implementation challenges, the move was aimed at reducing reliance on the dollar and attracting tech investment.
3. Institutional Investors
Hedge funds and asset managers such as Grayscale (with its Bitcoin Trust) have integrated Bitcoin into portfolios, indicating growing institutional confidence.
Risks and Challenges
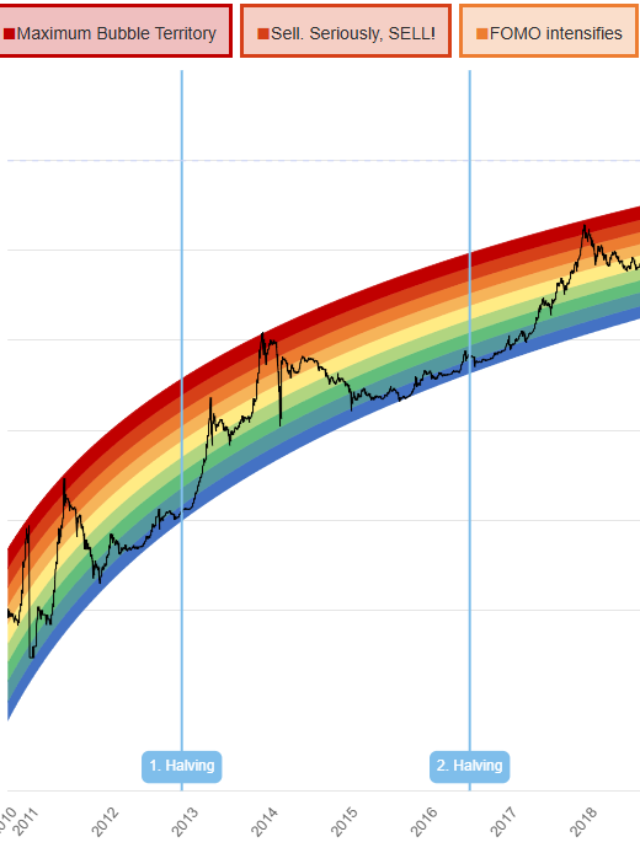
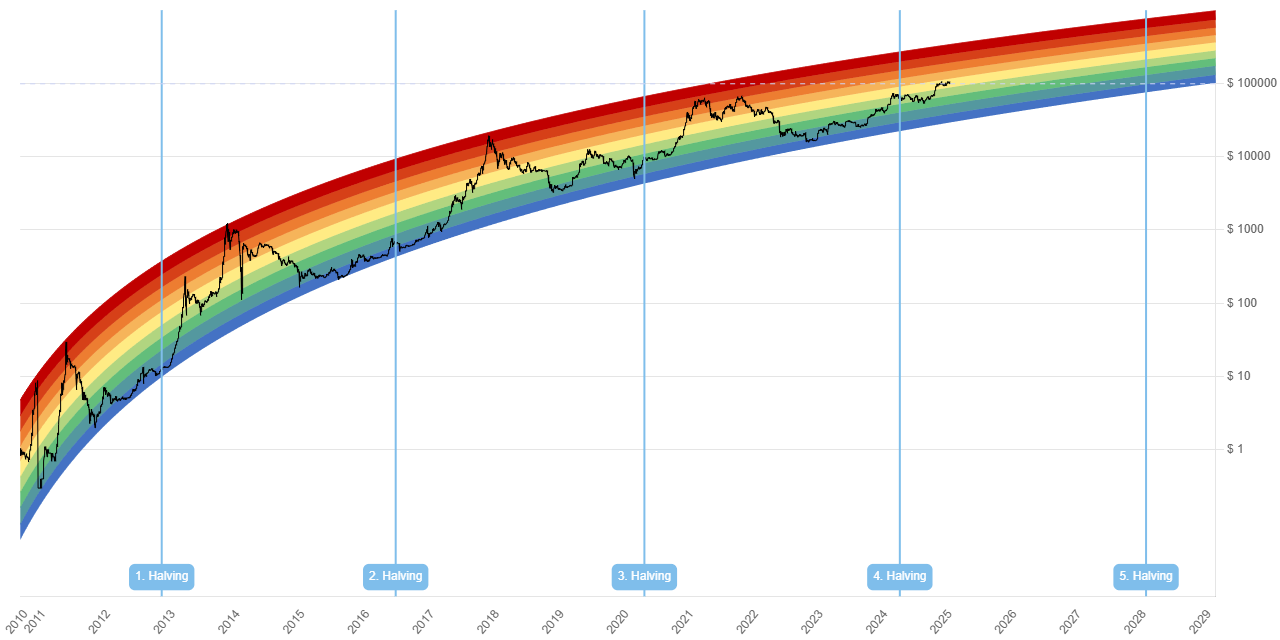
- Market Volatility Bitcoin price fluctuations can reduce reserve value. For example, the drop from $69,000 (2021) to $16,000 (2022) tested the resolve of holders.
- Regulatory Uncertainty
Governments may impose restrictions, as seen in China’s 2021 crypto ban. The SEC’s investigation of Bitcoin ETFs also impacts market sentiment. - Security Risks
Cyberattacks on exchanges (e.g., FTX’s 2022 collapse) expose vulnerabilities in custodial solutions. - Technical Risks
Software bugs, quantum computing threats, or network forks could undermine Bitcoin’s stability. - Environmental Concerns
Bitcoin mining’s energy consumption (~150 TWh annually) has drawn criticism. Transitioning to renewable energy and carbon credits is crucial for sustainability.

Benefits
- High Return Potential
Bitcoin’s CAGR of ~200% (2010–2020) outperformed traditional assets, though past performance doesn’t guarantee future results. - Inflation Resistance
In countries like Venezuela and Turkey, Bitcoin has preserved wealth amid hyperinflation. - Decentralization
Immunity to government interference or seizure (if stored properly). - Scarcity
The 21 million cap ensures scarcity, contrasting with fiat systems.
Future Outlook
Bitcoin’s role as a reserve asset hinges on broader adoption and regulatory clarity. Trends to watch include:
- ETF Approvals: Spot Bitcoin ETFs could democratize access.
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Potential competition or synergy.
- Technological Innovations: Layer-2 solutions (e.g., Lightning Network) enhancing scalability.
White House Recognizes Bitcoin as “Digital Gold”: Implications and Insights
Conclusion
A Bitcoin reserve strategy offers a high-risk, high-reward proposition, suitable for entities willing to navigate volatility and regulatory hurdles. While not a one-size-fits-all solution, its benefits—scarcity, decentralization, and inflation hedging—make it a compelling component of modern reserve management. Success demands meticulous planning, robust security, and a long-term perspective. As the financial ecosystem evolves, Bitcoin’s role in reserves may redefine global economic paradigms.